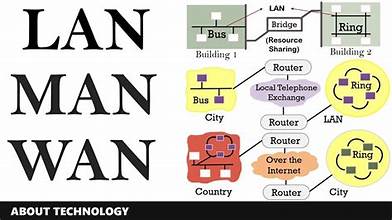
Sure, let’s break down LAN, WAN, and MAN:
- LAN (Local Area Network):
- LAN refers to a network that spans a small geographical area, typically within a single building or campus.
- It connects computers, servers, printers, and other devices to facilitate communication and resource sharing within a limited area.
- LANs are commonly used in homes, schools, offices, and small businesses.
- Ethernet and Wi-Fi are common technologies used to establish LANs.
- WAN (Wide Area Network):
- WAN is a network that covers a broad geographical area, connecting multiple LANs and other networks across long distances.
- WANs are used to connect computers and other devices over a wide area, such as between different cities, countries, or continents.
- The Internet is the largest and most well-known example of a WAN, connecting millions of devices worldwide.
- WANs often utilize various technologies, including leased lines, fiber optics, and satellite links, to transmit data over long distances.
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
- MAN is a network that spans a larger geographical area than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, typically covering a metropolitan area such as a city.
- MANs are used to connect multiple LANs within a city or metropolitan region, providing high-speed connectivity over a larger area than a LAN.
- MANs are often used by businesses, universities, and government agencies to interconnect their local networks and access shared resources and services.
- Fiber optic cables and wireless technologies are commonly used to establish MANs.
In summary, LANs are localized networks within a confined area like a building, WANs connect LANs over long distances, often globally like the Internet, and MANs bridge the gap between LANs and WANs, covering metropolitan areas.
Let’s delve deeper into each of these network types:
LAN (Local Area Network):
History:
- LANs have been around since the 1960s when researchers at MIT and other institutions began experimenting with early forms of computer networking.
- The development of Ethernet by Xerox PARC in the 1970s played a significant role in popularizing LAN technology.
- LANs became more widespread in the 1980s with the introduction of personal computers in homes and businesses.
Uses:
- LANs are used in various settings, including homes, offices, schools, and small businesses.
- They facilitate local communication and resource sharing among devices like computers, printers, servers, and storage devices.
- LANs are crucial for enabling tasks such as file sharing, printer sharing, and collaborative work within a confined area.
How They Work:
- LANs typically use Ethernet or Wi-Fi technologies to connect devices within a limited area.
- Ethernet involves connecting devices using cables, while Wi-Fi allows wireless connections.
- LANs often utilize network switches or routers to manage traffic and ensure efficient communication among devices.
- Devices on a LAN are usually connected to a central device, such as a router or switch, which controls the flow of data between them.
WAN (Wide Area Network):
History:
- WANs trace their roots back to the 1960s with the development of early packet-switched networks like ARPANET, the precursor to the Internet.
- The growth of telecommunications infrastructure, including telephone lines and satellite links, contributed to the expansion of WANs in the following decades.
Uses:
- WANs enable communication and data exchange over long distances, connecting geographically dispersed locations.
- They are used by organizations to interconnect their offices, branches, and data centers across different cities, countries, or continents.
- The Internet is the largest and most widely used WAN, providing global connectivity to millions of users and devices.
How They Work:
- WANs rely on various transmission technologies, including leased lines, fiber optics, satellite links, and wireless connections.
- Data on WANs often travels through multiple intermediate devices, such as routers and switches, before reaching its destination.
- WANs require protocols and standards to ensure compatibility and interoperability between different networks and devices.
- Security measures such as encryption and virtual private networks (VPNs) are essential for protecting data transmitted over WANs.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
History:
- MANs emerged in the 1980s as a response to the growing need for high-speed connectivity within metropolitan areas.
- They evolved from the integration of LAN and WAN technologies to provide fast and reliable communication over a larger geographical area.
Uses:
- MANs serve as a middle ground between LANs and WANs, connecting multiple LANs within a city or metropolitan region.
- They are used by businesses, universities, government agencies, and service providers to interconnect their local networks and access shared resources and services.
- MANs support applications such as video conferencing, cloud computing, and distributed computing, which require high-speed connectivity over a metropolitan area.
How They Work:
- MANs use a combination of technologies, including fiber optic cables, microwave links, and wireless connections, to cover a larger geographical area than LANs.
- They may incorporate network infrastructure owned by multiple organizations or service providers, requiring coordination and cooperation among stakeholders.
- MANs often rely on protocols and standards for efficient data transmission and network management.
- Security measures such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems are essential for protecting MANs from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
In summary, LANs facilitate local communication and resource sharing within a confined area, WANs enable long-distance communication and connectivity on a global scale, and MANs bridge the gap between LANs and WANs by providing high-speed connectivity within metropolitan areas. Each type of network has its own history, uses, technologies, and operational principles tailored to specific geographical and organizational requirements.




