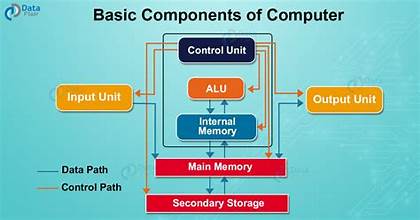
The basic components of a computer system include:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often referred to as the brain of the computer, the CPU performs instructions, carries out calculations, and manages data movement within the computer.
- Memory (RAM): Random Access Memory (RAM) is a type of volatile memory that temporarily stores data and program instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. RAM is cleared when the computer is turned off.
- Storage Devices: These devices store data and programs permanently or semi-permanently. Common types include Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), Solid State Drives (SSDs), and Flash drives.
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the main circuit board that houses the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and other essential components. It provides the physical connections and pathways for data to flow between components.
- Input Devices: These devices allow users to input data and commands into the computer. Examples include keyboards, mice, touchpads, and touchscreens.
- Output Devices: Output devices display information processed by the computer to the user. Common examples include monitors, printers, speakers, and projectors.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU provides electrical power to the computer components, converting alternating current (AC) from a power outlet into direct current (DC) usable by the computer.
- Expansion Cards: These cards are inserted into slots on the motherboard to provide additional functionality or connectivity to the computer. Examples include graphics cards, network interface cards (NICs), and sound cards.
- Cooling Systems: Cooling systems such as fans and heat sinks help regulate the temperature of computer components, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance.
- Operating System (OS): The operating system is a software program that manages computer hardware resources and provides a platform for running applications. Examples include Windows, macOS, and Linux.
These components work together to execute instructions, process data, store information, and interact with users, enabling the computer to perform a wide range of tasks and functions.




